 Getty Images
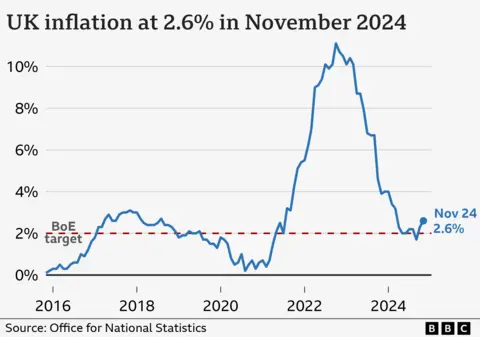
Getty ImagesThe UK inflation rate has gone up for the second month in a row, rising at the fastest rate since March.
The UK inflation rate rose to 2.6% in the year to November, according to official figures.
Fuel and clothing were among the main drivers behind the rise. Increasing ticket prices for gigs and plays were also a factor.
The Bank of England raises interest rates to try to keep inflation at its target of 2%. Its next rates decision is on Thursday, but economists expect rates to be held at 4.75%.
“Inflation rose again this month as prices of motor fuel and clothing increased this year but fell a year ago,” said Grant Fitzner, chief economist at the Office for National Statistics (ONS), which gathered the data.
“This was partially offset by air fares, which traditionally dip at this time of year, but saw their largest drop in November since records began at the start of the century.”
Chancellor Rachel Reeves said she recognised that families were still struggling with the cost of living.
“Today’s figures are a reminder that for too long the economy has not worked for working people.”
“I am fighting to put more money in the pockets of working people.”
Shadow chancellor Mel Stride said: “The chancellor has made a series of irresponsible and inflationary decisions.”
“These figures mean higher costs in the shops, less money in working people’s pockets and risks keeping mortgage rates higher for longer.”
Paul Dales, chief UK economist at the think tank, Capital Economics, said the figure “could have been worse”.
When combined with figures on Tuesday that showed faster growth in wages, he said it made it unlikely interest rates would be cut on Thursday.
“There is almost no chance of the Bank of England delivering an early Christmas present with another interest rate cut tomorrow, ” he said.
“That’s especially the case since domestic inflation pressures appear to be a touch stronger than the Bank expected.”
Capital Economics predicts inflation will dip in December and then rise again in January, but by the end of next year would have fallen back to close to the Bank of England’s 2% target.
A wider measure of inflation showed housing and household services costs, including rent, rose by 3.5%.

